Trusted Business Partner Data in the Age of AI

High-quality business partner data is the backbone of enterprise success in today's digital landscape. It's about having consistent, up-to-date information on customers and suppliers to drive critical decisions. And what about trust in this context? How can an organization make sure that everyone can trust the provided data?
We all know that trusted business partner data empowers organizations to uncover new opportunities, build stronger relationships, and enhance their market presence. Our key question is, where is this trust coming from?
What is Trusted Business Partner Data?
Trusted business partner master data contains vital information about customers and vendors/suppliers characterized by its source, accuracy, and timeliness. In our connected world, there are several external data types that contribute to building this trust:
-
Open Data: This category includes data accessible to all and can be used without restrictions. Valuable sources include governments, NGOs, and specific businesses. When evaluating business partners, databases containing registered entities' official names, addresses, and industries are paramount. For example, national postal service databases are instrumental in verifying vendor addresses, and trade registers are widely trusted due to their adherence to strict rules and legal requirements, such as tax number registers.
-
Paid Data: Specialized vendors provide paid datasets that highlight accuracy and freshness. These databases offer profound insights into potential customers or vendors, encompassing financial status and past activities. Renowned companies like Dun & Bradstreet and Bureau van Dijk offer comprehensive company profiles. However, trust levels in these providers can vary among organizations.
-
Shared Data: Shared data involves information exchange within dedicated platforms or communities. For instance, the CDQ Data Sharing community enables member companies to update shared information about common business partners - a network where all participants benefit. The SAP Business Network, a platform for data sharing and business network activities, also plays a pivotal role. However, trust in shared data can vary from company to company.
-
Web Data: Online sources, such as official websites, social media, and news sites, offer a wealth of insights. Trust in web data varies due to the vast and ever-changing nature of the internet. While some might trust data from well-known company websites, others cross-reference it with various sources for verification.
Trust in business partner data sources varies, with some, like trade registers, being widely trusted, while others require individual judgment. Organizations must navigate open, paid, shared, and web data to establish their level of trust and ensure a comprehensive and accurate view of their business partners.
Value creation of trusted business partner data along the data value chain
Having reliable customer and vendor master data is a priceless asset that can be the difference between success and failure in the corporate world. Continuously refining your data quality strategy, including data verification, validation, and enrichment, ensures that your business partner's data is always trusted. Building these trustworthy master data is often a collaborative effort. The comprehensive journey of data, right from its origin to its usage in strategic business planning, plays a vital role in an organization's achievements. The illustration highlights this data value progression, along with the corresponding data value formula. This formula effectively converts data into measurable business results.
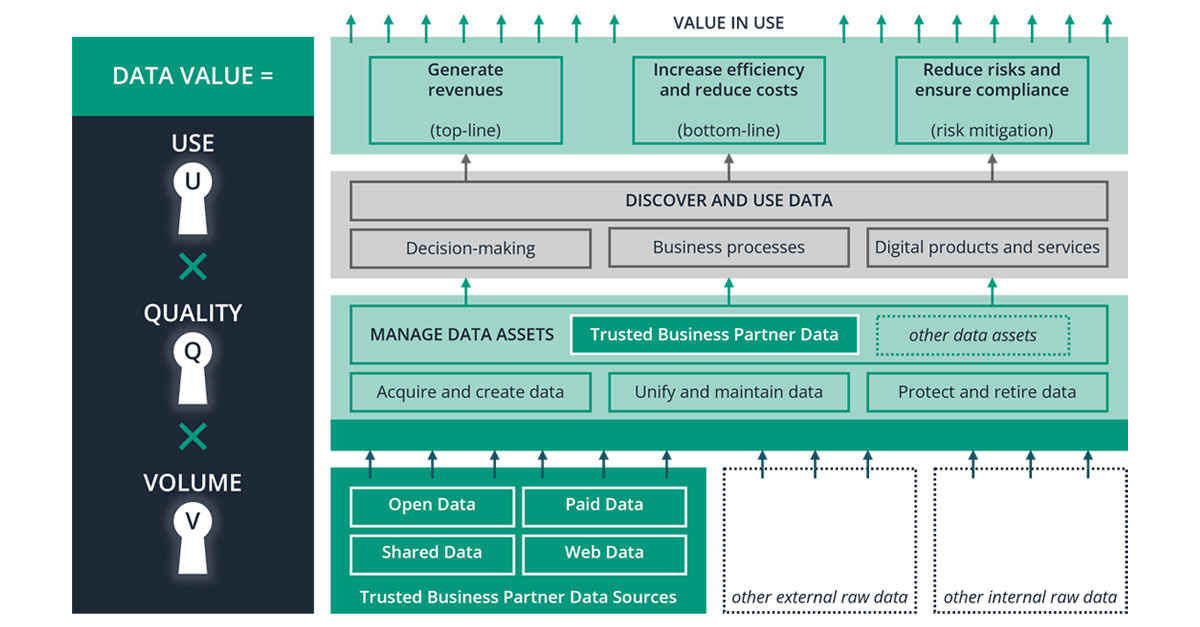
Trusted business partner data plays a pivotal role in optimizing processes, managing risks, and informing strategies. Its value can be summarized along the data value chain, from source to application:
-
Digitalization of Business Processes: Accurate business partner data is indispensable for streamlining processes in areas like procurement, supply chain, marketing, and sales. Errors resulting from poor data quality can significantly increase operational costs. As per the Tenfold Rule, rectifying poor data quality can cost ten times more than managing it correctly from the outset.
-
Risk Management and Compliance: Precise and consistent business partner data enables companies to effectively screen against sanction or embargo lists and adhere to crucial regulations. Quality data also aids in identifying potential financial and operational risks at an early stage.
-
Driving Business Insights and Leveraging AI: A harmonized view of business partner data across the organization facilitates in-depth analyses. This includes evaluating procurement volumes for refining sourcing strategies. Quality master data is critical for AI-driven techniques such as customer segmentation and supply chain optimization when integrated with other data sources.
-
Integration with External Data Sources: Merging business partner data with other data types can yield deeper insights. For instance, combining supplier data with market insights may reveal concealed market opportunities.
-
Data Quality as an ROI Multiplier: Reliable business partner data ensures that insights derived from it are dependable, leading to more effective strategies and optimized returns, especially in marketing campaigns built on accurate data.
-
Empowering Digital Strategies: Quality vendor data streamlines e-commerce processes, while dependable customer data enhances personalization, fostering customer loyalty.
-
Fostering Collaboration and Innovation: When businesses trust the accuracy of shared data, they are more likely to collaborate, resulting in innovative solutions and offerings.
Trusted Business Partner Data in the Age of AI
In the era of AI and Emerging Technologies, obtaining trusted business partner data is crucial. This data acts as a pillar that supports AI and drives accuracy in its results. By harnessing the power of trusted data from business partners, organizations can build robust machine-learning models capable of generating insightful, accurate predictions and trend analysis. This guides strategic decision-making, ultimately leading to increased productivity and business growth.
Business applications that involve predictive tasks, like forecasting market trends or identifying consumer tastes, greatly rely on the caliber of the data utilized. Machine learning algorithms that are fed with well-detailed and superior-quality data from reliable business partners have a higher chance of providing precise outcomes, compared to those that are based on less credible data.
When we talk about trust in data, it goes beyond mere correctness of information. Data needs to be trusted, not just for its accuracy, but also for its source and compliance with specific standards. If your data originates from a reputable place, meets all necessary legal prerequisites, and is in line with ethical concerns, it's held in a higher esteem. Organizations making decisions based on these kinds of data ultimately reflect a sense of accountability and integrity in their operations.
As the world of business gets more intertwined and reliant on data, it's integral to ensure the authentication and ethical gathering of that data. No matter the impressive capabilities of AI, it cannot autonomously assess these aspects of information. AI might be capable of analyzing massive data and spotting trends, yet it lacks the innate ability to judge if the data was obtained ethically or whether its source is genuine.
It's important to acknowledge that despite the leaps and bounds we're seeing in the realm of artificial intelligence (AI), the human touch remains irreplaceable. While AI continues to automate a growing number of our tasks, the task of ensuring that the data we rely on is dependable remains a distinctly human duty. As our reliance on AI for decision-making accelerates, the necessity to validate the quality of the data we give it becomes fundamental. Any effective partnership between humans and AI stems from data quality and integrity. Therefore, it's vital to remember that no matter how advanced our tech becomes, humans continue to hold a unique and imperative role in authenticating the integrity of that data.
Key Takeaways
Trusted business partner data is essential for businesses, offering correct, accurate, and timely information about customers and vendors. Its significance extends beyond accuracy and encompasses transparency in data origin and the availability of trusted sources. In an AI-driven landscape, ensuring data trustworthiness is essential for making informed decisions and achieving reliable outcomes.
Trusted business partner data is a valuable asset, serving as a foundation for success in modern enterprises. Hence, in the world of business, trust is not just an intangible concept but an invaluable resource that enables business partnerships to prosper and grow.
Continue the journey with trusted business partner data and explore further links:
- Trustworthy business partner data through data sharing (erp-informarion.de article in German)
- Data Value Formula (ebook download)
- Trusted business partner data and SAP (SAP Blog)

Get our e-mail!
Related blogs
Stepping out of silo thinking: Henkel’s data quality story
A refreshing look at how Henkel tackles an immensely complex data landscape: candid disussion with master data experts, Sandra Feisel and Stefanie Kreft.
The e-invoicing reality: the gateway is ready, but is your data?
Over the past decade, the EU has steadily shifted from encouraging electronic invoices to mandating them. And while the technology obviously plays an important…
How Henkel is turning master data quality into a service
Every now and then, you come across a project that makes you stop and think: “Now that’s how it should be done!” That’s exactly the case with Henkel and their…